跟着顶刊学分析之随机森林

本示例参考Prophage-encoded antibiotic resistance genes are enriched in human-impacted environments
随机森林是一种强大的数据挖掘工具,能够处理高维度、多变量且复杂相关的数据,在本研究中帮助揭示了哪些人类相关活动(如抗生素使用、经济发展、农业生产等)最能解释`ARGs`在不同环境中的分布差异。这篇发表在 Nature Communications 的文章,通过结合大规模多组学数据与随机森林建模,不仅深化了我们对噬菌体在抗生素耐药性扩散中作用的理解,也为全球抗生素耐药风险的评估和干预提供了新的视角和工具。结果显示,人类活动显著促进了前噬菌体携带耐药基因的富集,这些基因不仅数量更多,而且更容易在不同生态系统间转移和表达。进一步的实验证明,这些由前噬菌体携带的耐药基因可以实际赋予宿主细菌抗药性。
随机森林建模
加载包和数据
1 | # 加载所需要的包 |
读取数据文件,包含细菌 ARGs 数据和 13 个环境或微生物群落特征。
查看数据
1 | # 查看数据 |
数据包括相应变量HH.ARG;预测变量为前 13 个环境或微生物群落特征。
数据拆分
1 | # 设置随机种子,用于重复 |
随机抽取 30% 的行作为测试集(Test Data),剩余 70% 作为训练集(Train Data)。
将数据分为训练和测试集,用于模型训练和性能评估。
随机森林建模
1 | # Random forest modeling using the first 13 principal components to predict HH.ARG |
建立模型预测 HH.ARG,并准备评估变量重要性。
说明:
- 使用 randomForest 包构建随机森林回归模型
- 相应变量: HH.ARG
- 预测变量: 训练集中除 HH.ARG 外的所有列
- ntree = 500: 构建 500 棵决策树
- importance = TRUE: 计算变量重要性
- nPerm = 1: 置换检验的重复次数
nPerm:
`nPerm`作用是在指定在评估变量重要性时,对每棵树的 OOB(Out-of-Bag)数据 进行置换的次数(仅用于回归问题,分类问题时候不支持)。默认值`nPerm = 1`,表示每次只进行一次置换。当`nPerm > 1`时,每次计算变量重要性时会多次置换 OOB 数据,取平均结果,从而提供更稳定的重要性估计。但置换次数并不是越高越好,增加 nPerm 会提高计算成本,但对结果的稳定性提升有限,次数差不多就行,例如 1000 此;同时仅影响重要性计算,不影响模型的预测或拟合。
模型预测和性能评估
评估模型在测试集上的预测性能。
1 | # Predictions |
MSE(均方误差):预测值与实际值差的平方平均,值越小表示模型越准确。
R²(决定系数):1 - MSE / 方差,表示模型解释的变异比例,值接近 1 表示模型拟合好。
因子显著性分析(置换检验)
1 | # Use the rfPermut() function to re-perform random forest analysis on the above data |
使用`rfPermute`包进行置换检验,评估预测变量的重要性显著性。
HH.ARG ~ . 与之前模型相同,使用所有预测变量预测 HH.ARG
提取重要性分数
1 | # Extract importance scores of predictive variables |
提取变量重要性分数,并进行标准化(scale = TRUE),量化每个主成分对模型的贡献及其统计显著性。
按重要性排序
1 | # Sort predictive variables by importance scores, e.g., by "%IncMSE" |
按`%IncMSE`降序排序重要性数据框,优先展示最重要的变量,便于可视化时突出关键预测变量。
绘制重要性柱状图
1 | # Plotting the %IncMSE values of predictive variables |
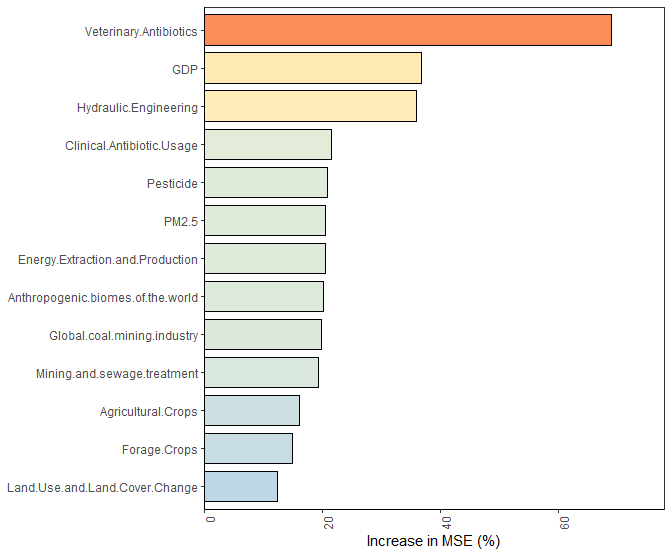
可视化主成分对模型的重要性,直观展示哪些变量对预测HH.ARG贡献最大。
添加显著性标记
1 | # Mark the significance information of predictive variables |
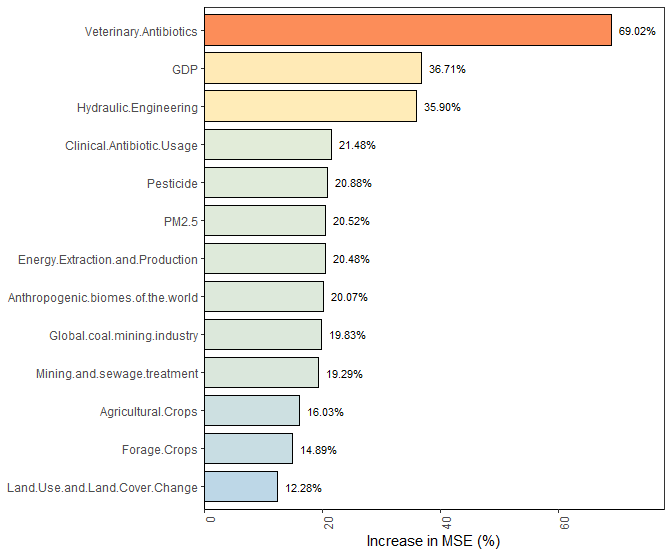
突出显著变量,帮助解读哪些主成分对模型的贡献在统计上显著。
模型整体显著性评估
1 | # A3 package for evaluating model p-value |
验证模型整体是否显著(p < 0.05 表示模型预测能力超出随机水平)。
添加模型统计信息到图表
1 | # Add known explanation rate of the model to the top right corner |
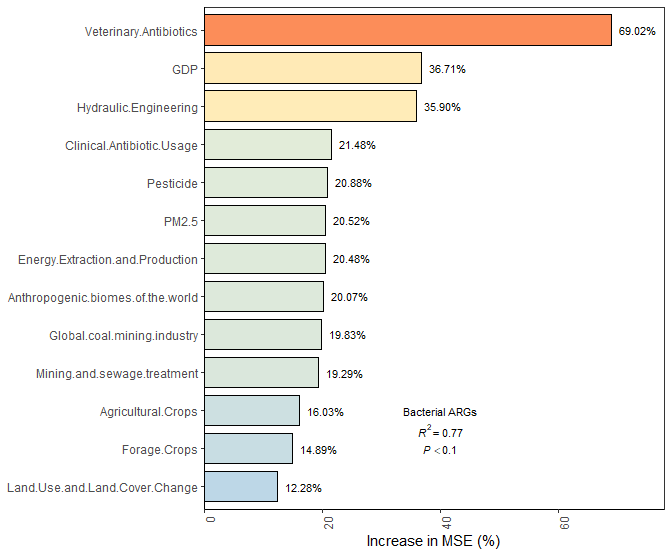
总结模型性能,增强图表的信息量。
注意事项和改进建议
但如果计算资源允许,可增加置换次数 1000 到 5000 以提高 p 值精度。
当前仅计算了测试集的 MSE 和 R²,建议添加交叉验证:
1 | suppressMessages(suppressWarnings(library(caret))) |
总结
这段代码通过随机森林模型分析细菌 ARGs 与主成分的关系,评估模型性能,并可视化变量重要性。主要步骤包括:1. 构建和评估随机森林模型(MSE, R²);2. 通过置换检验确定主成分的显著性;3. 绘制柱状图,展示 %IncMSE 和显著性标记,添加模型统计信息。
代码简洁版
1 | # 加载所需要的包 |
版本信息
1 | sessionInfo() |
- Titre: 跟着顶刊学分析之随机森林
- Auteur: Xing Abao
- Créé à : 2025-04-27 13:22:55
- Mis à jour à : 2025-10-22 12:15:26
- Lien: https://bioinformatics.vip/2025/04/27/SCI/250427_sci_random_forest/
- Licence: Cette œuvre est sous licence CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.